Which Best Describes Signal Conduction In Unmyelinated Axons Neural Impulse On Emaze
What is true about signal conduction along myelinated fibers? A local potential is passively conducted down the entire length of the axon. Which best describes signal conduction in unmyelinated axons?
Solved Which best describes signal conduction in
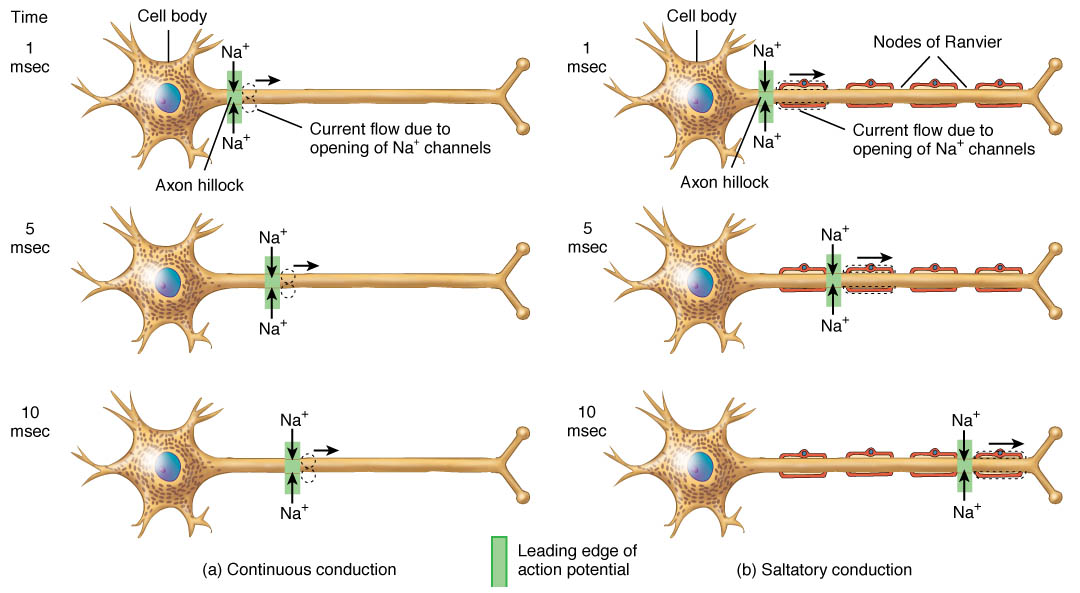
Which best describes signal conduction in unmyelinated axons? Extracellular signaling the extracellular signals that propagate through the extracellular matrix surrounding neurons play a prominent role in axonal development. The action potential travels by jumping between nodes of ranvier.
A local potential is passively conducted down the entire length of the axon.
Which best describes signal conduction in unmyelinated axons? Unmyelinated axons conduct nerve impulses via saltatory conduction. Signal conduction in unmyelinated axons is primarily described as continuous conduction. The ability of a neuron, to enhance the effect of another neuron.
Unmyelinated axons lack the insulating myelin sheath that. Which best describes signal conduction is unmyelinated axons? An influx of calcium ions causes immediate repolarization. Which best describes signal conduction in unmyelinated axons?

In this process, the action potential, or electrical signal, travels along the axon.
Which best describes signal conduction in unmyelinated axons? Unmyelinated axons employ a continuous conduction mechanism, where electrical signals move along the entire length of the axon. Which best describes signal conduction in unmyelinated axons? A local potential is passively conducted down the entire length of the axon.
The entire axon depolarizes at the. Match each gilal cell type with its location and function: The entire axon depolarizes at the same time. Satellite cells, schwann cells, ependymal cells, and microgilia.

Here are 7 key points about conduction in unmyelinated axons:
Which term is used to describe signal conduction along a myelinated axon? The signal is transmitted from one node of ranvier to the next through saltatory conduction. However, due to the absence of myelin. Signal conduction along myelinated fiber.