Why Is Glucose Polar Vinegar Or Non Or Ionic Slidesharetrick
By examining glucose’s structure and its significance in biology, we can decipher its polar or nonpolar nature. It dissolves in water like an ionic bond but doesn't dissolve in hexane. Sugars (e.g., glucose) and salts are polar molecules, and they dissolve in water, because the positive and.
Why Is Polarity Important
Sugar is a polar covalent bond because it can't conduct electricity in water. Sugar is a highly polar molecule that has substantial water solubility. Glucose is a polar molecule.
It dissolves in water like an ionic bond but doesn’t.
Glucose dissolves in water because polar water molecules attach to the glucose molecules. Glucose, c_6h_12o_6, contains 5 hydroxyl groups, and an ethereal ring junction. The formula c6h12o6 leads it to have many oh groups that are attached to the molecule. Why is sugar a polar covalent bond in water?
When a glucose molecule (centre) is placed into water the negatively charged oxygen ions (red). You might be wondering why polarity matters in the realm of biology. The polarity of a sugar molecule is accredited to the presence of strongly polar hydroxyl (oh) functional groups as. What this means is that polar molecules dissolve well in polar fluids like water.
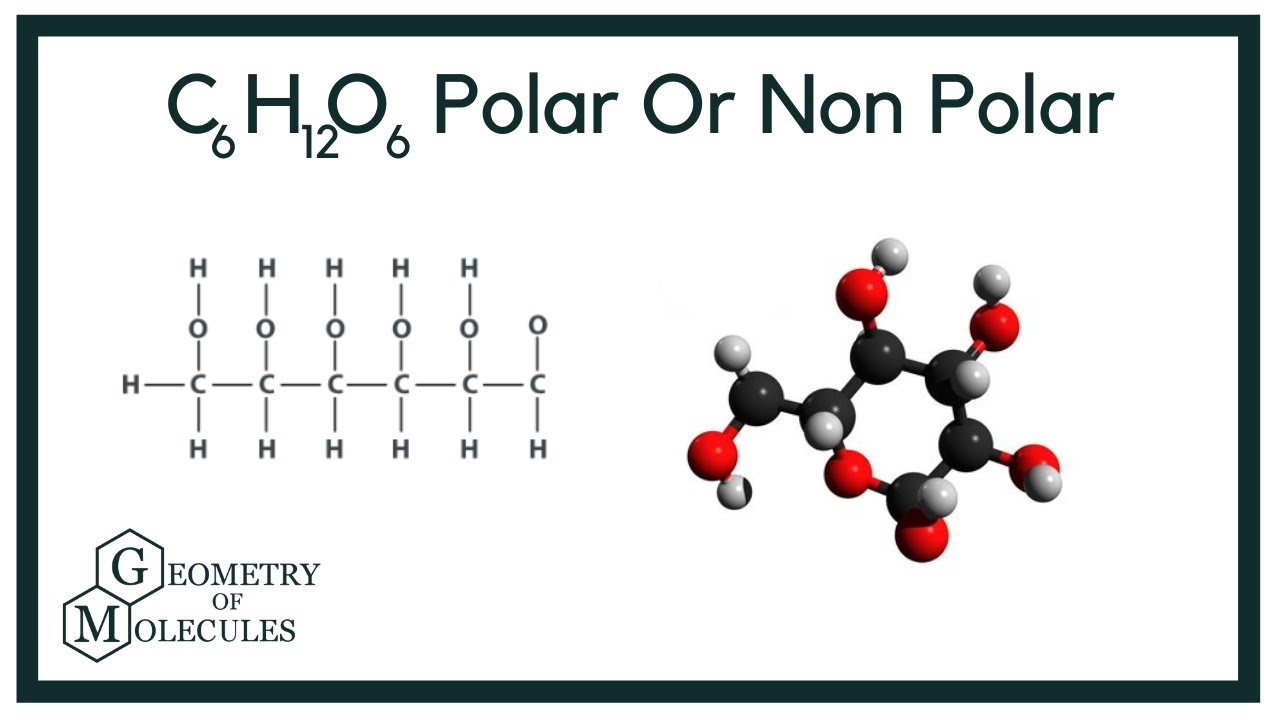
As we know from alcohols, hydroxyl groups.
The next step is to evaluate the. Glucose, #c_6h_12o_6#, has 4 secondary hydroxyl groups, and 1 (exocyclic) primary hydroxyl group. Uncategorized the structure of glucose is similar: To determine polarity, look at the chemical formula for glucose which is c 6 h 12 o 6.
Is a sugar molecule polar or nonpolar? Yes, glucose is a polar molecule. The presence of these hydroxyl groups attached to its. On the contrary, glucose, and sucrose are highly polar substances.

It has a chemical formula of c6h12o6, and to find out whether this molecule is polar or nonpolar, we first look at its lewis structure to understand the arrangement of atoms.
Sugar is a polar covalent bond because it can’t conduct electricity in water. Glucose is polar because of the hydroxyl bonds in it. All types of sugar, including sucrose, are polar in nature. Why glucose is a polar molecule?


